What is solar PV?
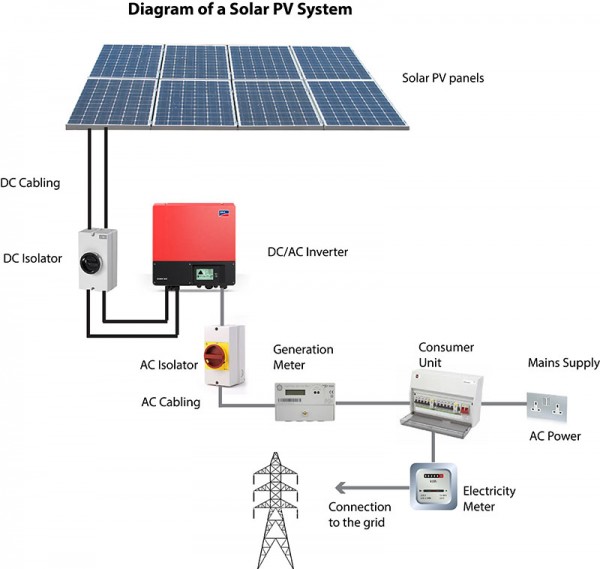
Solar cells, also called photovoltaic (PV) cells by scientists, convert sunlight directly into electricity. PV gets its name from the process of converting light (photons) to electricity (voltage), which is called the PV effect. The PV effect was discovered in 1954, when scientists at Bell Telephone discovered that silicon (an element found in sand) created an electric charge when exposed to sunlight. Soon solar cells were being used to power space satellites and smaller items like calculators and watches. See below a typical Solar PV layout.
Installing Solar PV Panels
For the installation of Solar PV panels, a clear, uninterrupted and unshaded section of roof is required, with south or near south orientation. The roof needs to be large enough to accommodate the Solar PV modules, structurally sound and built using materials that are compatible with a fixing system that is readily available.
Feed-In Tariffs
Direct or diffuse light shining on the Solar PV cells induces the photovoltaic effect, generating direct current (DC) electrical power. This electricity can be converted to alternating current (AC) power for use in the building or it can be exported to a utility company through the national grid connection. Under the UK government Feed in Tariffs scheme (Clean Energy Cashback) qualifying individuals or groups who install Solar PV can benefit from regular payments.